(Bloomberg) — Aluminum climbed to the highest in more than a decade after a coup in Guinea fueled concerns over raw material supplies, at a time when global output is already constrained and demand is booming.
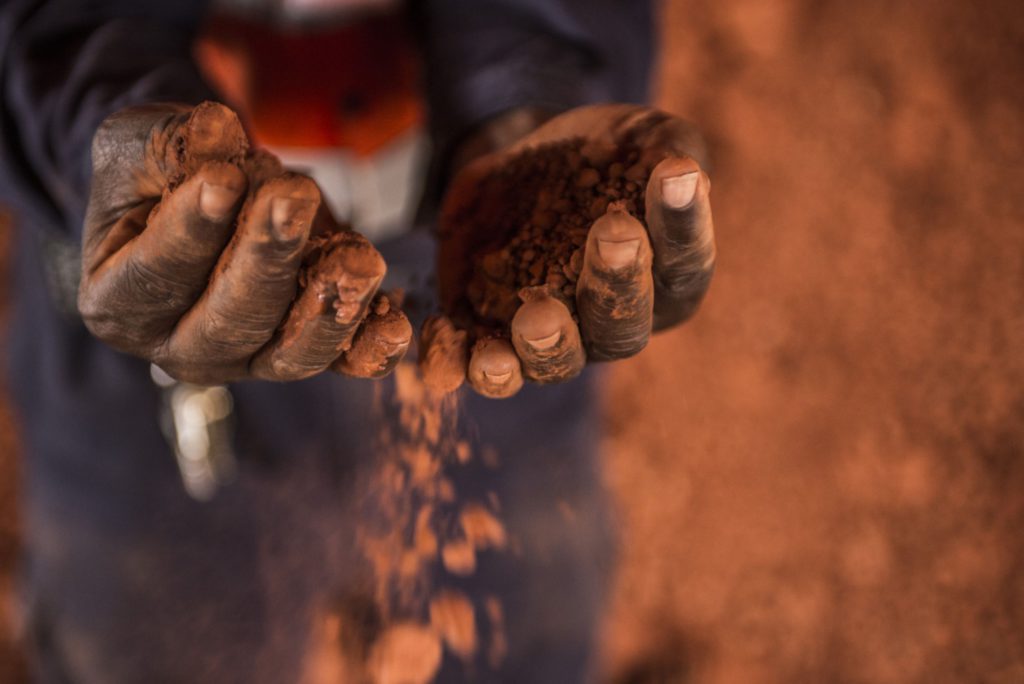
Aluminum prices gained in London and Shanghai and producers’ shares surged — industry leader Aluminum Corp. of China, or Chalco, jumped as much as 10%, while United Co. Rusal traded 15% higher. Guinea is a major supplier of bauxite, the feedstock needed to make aluminum, and accounts for more than half of the imports by China.
A unit of the military seized power Sunday and suspended the constitution, with head of special forces, Colonel Mamady Doumbouya, urging the army to back him. While the unrest raises the possibility of disruption, so far there’s no sign that shipments or mines have been affected. Chalco, which has a bauxite project in Guinea, said all of its operations are normal and it has ample bauxite inventories at its plants in China.
Aluminum, which is used in everything from car parts to drinks cans and home appliances, had already climbed about 38% this year in London before the coup, as consumer demand and economic activity rebound. At the same time, smelters in China have struggled to maintain output during a seasonal power crunch and as Beijing seeks to rein in the country’s carbon emissions.
While Rusal founder Oleg Deripaska warned that the market “can be seriously shaken” by the situation, traders were still waiting on Monday for further clues about potential supply cuts.
The bauxite market has been in surplus for years, and any disruption would need to be severe to alter that dynamic, according to Michael Widmer, head of metals research at Bank of America Merrill Lynch.
“I’m bullish aluminum, but for different reasons,” Widmer said by phone from London. “That said, if you do have issues in a country that supplies 20% of bauxite to the global market, then clearly that will be a problem.”
Prices on the London Metal Exchange rose as much as 1.8% to $2,775.50 a ton, the highest since May 2011, and traded at $2,756.50 as of 10:34 a.m.. In China, futures jumped as much as 3.4% to the highest since 2006, before paring gains to 2.2%. Other industrial metals were mixed on the LME, with copper little changed and nickel down 1.8%.
“Investors are quite concerned given China buys a big chunk of bauxite from Guinea,” though there haven’t been reports of disruptions yet and the extent of any impact will depend on how the situation evolves, said Xiong Hui, chief aluminum analyst with Beijing Antaike Information Development Co.
Investors are also looking at ongoing production cuts in China’s Guangxi province, which is further tightening the market, Hui said.
The energy-intensive aluminum industry has come under increased scrutiny as part of Beijing’s pollution crackdown. China produces around 60% of the world’s total, with concerns around output prompting some of its largest smelters to pledge to ensure supply, and metal to be released from state reserves to ease tightness. The country has become increasingly reliant on imports, a rare development that’s drained global supplies of the usually abundant metal.
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.