A Turkish court on Monday extended the detention of a civil society leader whose case has set Ankara on a collision course with Europe’s top human rights body and Western allies.
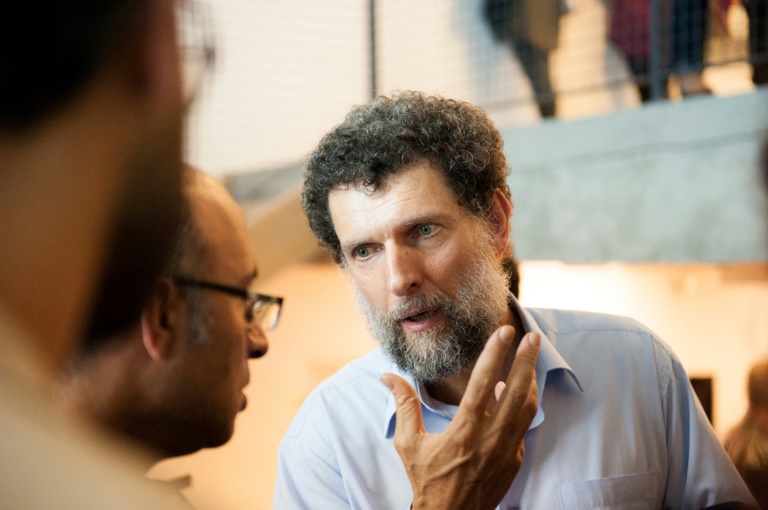
Philanthropist Osman Kavala has been held without a conviction since October 2017 for allegedly financing 2013 anti-government protests and playing a role in an attempted coup against President Recep Tayyip Erdogan in 2016.
The 64-year-old’s supporters view his plight as a symbol of the purges Erdogan unleashed after the coup attempt.
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) first ruled Kavala’s detention to be politically motivated in December 2019.
The Council of Europe — a human rights organisation Turkey joined in 1950 — followed that up by launching formal infringement proceeding against Ankara last month.
It also gave Turkey until Wednesday to either release Kavala or provide legal justification for keeping him behind bars.
The Istanbul court did neither at a hearing Monday attended by observers from the European Union and nine Western countries.
The court set the next hearing for February 21.
“It is very disappointing,” Emma Sinclair-Webb of Human Rights Watch (HRW) told AFP after the hearing.
“President Erdogan seems willing to be subjected to the sanction process,” she added. “This is very destructive for Turkey and international rights law.”
– Diplomatic standoff –
Kavala’s case has become a growing irritant on Turkey’s complex ties with the West.
An appeal from 10 Western countries last October — including the United States and major European powers — for Turkey to release Kavala triggered a diplomatic standoff that nearly saw Ankara expel their ambassadors.
The German government stressed on Monday it was closely following the case.
“We will direct our attention to the hearing in Istanbul together with the many people who care about the protection of human rights in Europe,” the German government’s commissioner for human rights said in a statement tweeted by the embassy in Ankara.
The Council of Europe’s infringement procedures against Turkey could last months and possibly years.
But they could ultimately see Turkey lose its voting rights or even kicked out of the pan-European rights body.
Turkey’s foreign ministry said it views the Council’s actions — only launched once before against any of its 47 member states — as “interference” in an ongoing court case.
Government critics say Turkey’s standoff with the body underscores the profound erosion of human rights under Erdogan’s two-decade rule.
HRW last week warned that Erdogan “has set back Turkey’s human rights record by decades” by undermining judicial independence and targeting his critics.
It also pointed to Turkey’s withdrawal last year from a convention protecting women against domestic violence and Erdogan’s “rollback” of LGBTQ rights.