(Bloomberg) — President Joe Biden and Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida condemned North Korea’s launch of what they said was a long-range ballistic missile, a provocation that came as the two leaders met with other allies in Brussels to confront the Ukraine crisis.
Biden and Kishida “strongly condemned” the launch, North Korea’s first test of such a weapon in more than four years, “stressed the need for diplomacy, and agreed to continue working together to hold the DPRK accountable,” the White House said in a statement, using an acronym for North Korea’s government.
The U.S.
and Japanese leaders met on the sidelines of a Group of Seven summit, one of three meetings with allies Biden is attending in Brussels on Thursday.
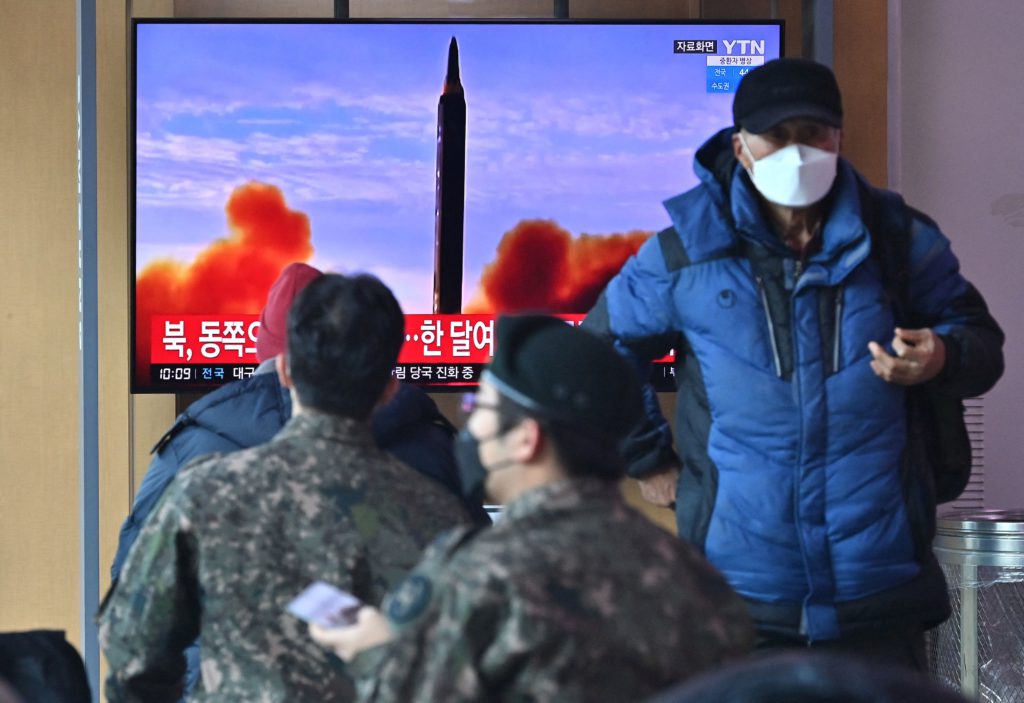
The intercontinental ballistic missile was launched from the Sunan area outside Pyongyang on Thursday, reaching an altitude of 6,200 kilometers (3,900 miles) and traveling 1,080 kilometers, South Korea’s Joint Chiefs of Staff said.
That’s higher and farther than North Korea’s last ICBM test in November 2017, suggesting that North Korean leader Kim Jong Un had successfully launched a long-anticipated weapon believed to be capable of carrying multiple nuclear warheads.
The launch represented Kim’s abandonment of a testing freeze that had underpinned an unprecedented wave of talks with the U.S.
under former President Donald Trump. The negotiations ultimately unraveled and have not been revived under Biden, though his administration has said it’s open to talks with Kim’s government.
North Korea typically doesn’t comment on its tests until the next day.
The country has described recent rocket tests from the same area as efforts to launch a satellite.
“This launch is a brazen violation of multiple UN Security Council resolutions and needlessly raises tensions and risks destabilizing the security situation in the region,” White House Press Secretary Jen Psaki said in a statement.
“The door has not closed on diplomacy, but Pyongyang must immediately cease its destabilizing actions.”
The self-imposed testing freeze helped de-escalate a crisis in which Trump threatened to unleash “fire and fury” against North Korea and ultimately paved the way for talks between the two leaders.
The last time North Korea conducted such a test, in November 2017, China and Russia supported a U.S.-led effort to impose crippling sanctions on the country.
A similar effort by Biden is unlikely now, as Beijing and Moscow oppose the international sanctions campaign over Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
“I believe they have completed the creation of the Hwasong-17, the so-called ‘monster missile,’” said Yang Moo-jin, professor at the University of North Korean Studies in Seoul.
“They would cite two reasons for scrapping the moratorium: No further change of stance from Washington. And a firm belief that denuclearization will only lead to destruction, based on what they are seeing from the Ukraine crisis.”
North Korea rolled out the Hwasong-17 at an October 2020 military parade.
The weapon appears to be the world’s largest road-mobile ICBM and is designed to carry multiple warheads in a bid to overwhelm American missile-defense systems.
The projectile landed inside Japan’s exclusive economic zone, about 150 kilometers off the coast of Hokkaido prefecture, Japan’s defense ministry said.
The rocket was aloft for about an hour.
Earlier, Kishida called the test “outrageous” and said his country would consult with the U.S. and South Korea on a response. South Korean President Moon Jae-in “strongly condemned” the launch and his military test-fired a volley missiles in response to demonstrate its own ability to strike.
Moon had dedicated much of his tenure to improving ties with North Korea, including holding three landmark meetings with Kim.
The moratorium was one of the last remaining achievements of that effort by Moon, who leaves office in May.
His successor, President-elect Yoon Suk Yeol is a conservative who said on the campaign trail that he would consider a preemptive strike to prevent an imminent attack by North Korea.
Yoon’s transition team called Thursday’s launch a “grave provocation.”
China Foreign Ministry spokesman Wang Wenbin called for restraint, without criticizing North Korea. “We hope that all parties can keep in mind the big picture of peace and stability of the peninsula, stick to the right direction of dialogue and consultation, and work together for the political settle of the peninsula issue,” Wang told a regular news briefing in Beijing.
Nuclear Sites
North Korea has ramped up activity at key missile and nuclear weapons sites since signaling in January that he might end the testing freeze and South Korea and the U.S.
had recently detected signs of an ICBM launch. The country also appears to be undertaking construction work at its main nuclear weapons test site for the first time in about four years.
On March 16, North Korea fired a suspected ballistic missile from an the Sunan area, near Pyongyang’s international airport.
South Korea’s military believes the test ended in failure with the missile exploding before reaching an altitude of 20 kilometers, Yonhap said.
The U.S. had said that earlier North Korean launches on Feb.
26 and March 4 that were also from the area around the Pyongyang airport were intended to test elements of the new ICBM. North Korea had described the launches as an effort to develop its satellite program, something it argues its entitled to do.
Chang Young-keun, a missile expert at the Korea Aerospace University, said North Korea’s latest ICBM was more powerful than the one launched in 2017.
“It’s not just that they have broken the moratorium, but they have crossed the line,” Chang said. “North Korea wanted the U.S. to make concessions on the sanctions front and South Korea to play the ‘mediator role,’ but didn’t work out at all.
So Pyongyang has no choice but to ratchet up tensions.”
(A previous version of this story corrected the prefecture near where the missile fell.)
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.