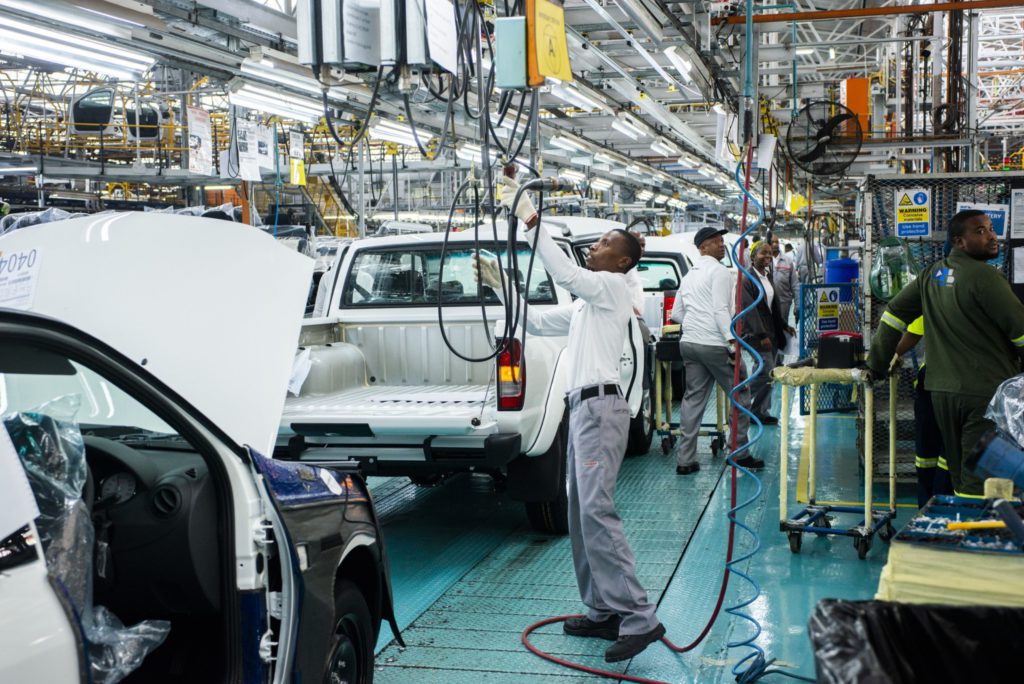
(Bloomberg) — South Africa risks losing the bulk of its automotive exports unless the government implements policies to create an electric-vehicle manufacturing industry, according to Nissan Motor Co.’s Africa head.
Europe is the destination for about two-thirds of car exports from South Africa, which earned 202 billion rand ($14 billion) from sending vehicles and components internationally in 2019. But with countries such as Germany moving toward mandating the use of cleaner cars, South Africa risks being left behind, Mike Whitfield, Nissan Africa’s managing director, said in an interview.
“A very large percentage of our exports as an industry go to Europe, and while Europe is moving aggressively to electric, we are not,” said Whitfield, who is also president of the African Association of Automotive Manufacturers. “We are going to progressively lose our potential markets.”
South Africa relies on the automotive industry for about 15% of its exports, and has lured major manufacturers such as Toyota Motor Corp. and Volkswagen AG with a government incentive plan to set up local plants. Yet the country remains a long way off introducing electric vehicles to its roads on any significant scale. While traditional gas and diesel-fueled cars can be imported for free, EVs attract a duty of as much as 25% and there are few charging stations.
“You are not going to get industrialization of electric vehicles unless you’ve got demand,” Whitfield said. “We need the charging infrastructure” and incentives to buy, he said.
The rest of Africa has also been slow to foster production, including in carmaking strongholds such as Egypt and Morocco, he said.
African Potential
One cause for optimism in Africa is that new car sales are expected to grow to as many as 5 million a year in 2035 from 1.2 million, and that could compensate for declines in the European export market, he said.
“The intention is to transition and keep the market in Europe, which obviously requires investment and some changes in policy and approach,” Whitfield said. “Add to that the potential of the African market.”
Nissan this month opened an assembly plant in Ghana, with components supplied by plants in South Africa, and is considering entering East Africa with a partner, he said.
Nigeria — Africa’s most populous nation with more than 200 million people — isn’t likely to contribute to growth of the continent-wide market due to the mass import of used cars. An automotive policy that included duties on second-hand vehicles was never fully implemented and new car sales have plunged to as little as 10,000 a year.
“We’ve got to keep addressing affordability,” Whitfield said. “Right now used vehicles fulfill that role.”