The dollar is headed into 2023 on a more downbeat note as the pace of Federal Reserve interest-rate hikes begins to slow amid signs that inflation risks are beginning to lessen.
(Bloomberg) — The dollar is headed into 2023 on a more downbeat note as the pace of Federal Reserve interest-rate hikes begins to slow amid signs that inflation risks are beginning to lessen.
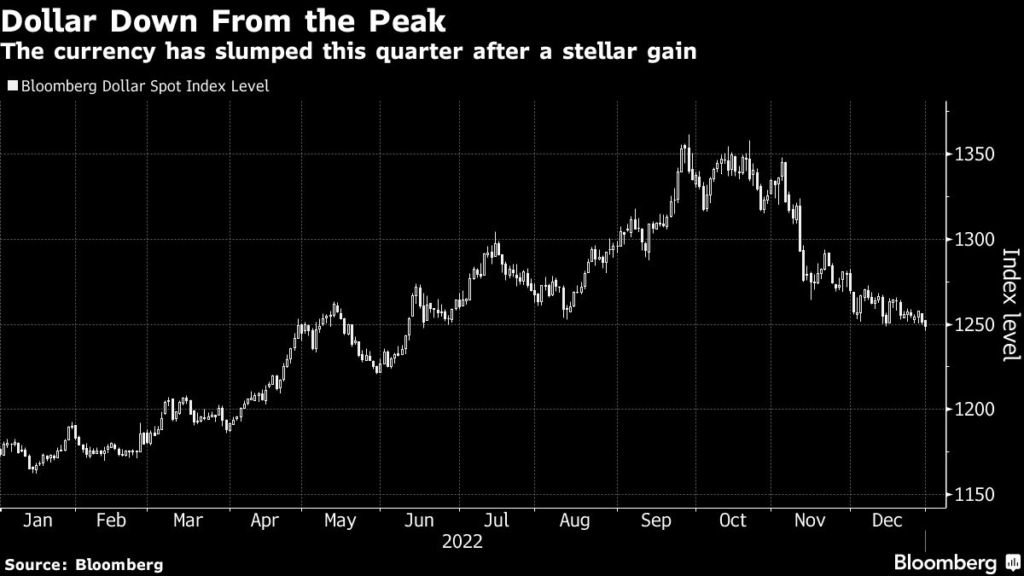
The Bloomberg dollar index notched biggest quarterly decline since 2010 and trading around its lowest level in six months after beating a hasty retreat from the record high it hit on Sept. 28. It slid another 0.4% Friday, the year’s final trading day, at one stage reaching the lowest mark since June. Yet while the greenback is down more than 8% from its peak, the currency is still up more than 6% since the end of 2021, the best year-on-year performance for the gauge since 2015.
Among Group-of-10 currencies, the New Zealand dollar and the Norwegian krone have been the standouts this quarter, each climbing more than 10%. But perhaps the most notable about face has been the yen, which has rebounded sharply in the wake of a policy shift from the Bank of Japan, whose surprise December decision to tweak its yield curve control settings is seen by many as a sign that the country’s ultra-easy settings might soon be coming to an end.
For the dollar more broadly, though, it has been — and will continue to be — the path of Fed policy that’s most critical — and how that stacks up relative to other central banks. Runaway inflation earlier this year led the Fed to implement a series of supersized rate increases that lifted the greenback. With officials slowing the pace of hikes at their meeting this month and expectations for how high the Fed might go with its benchmark dipping back to around 5%, some of that pressure has abated — for now at least.
The appetite for the dollar was also helped by haven flows, among other factors, as concern about the tightening of global policy weighed on riskier assets along with heightened geopolitical tensions and ongoing concerns around Covid. The possibility of a US recession, risks around China’s Covid reopening, and the possibility of further declines in stocks, of course, have the potential to reinvigorate the appeal of the US currency at some point. For now though, the trend is down, and all eyes will be on how the economic and market landscape plays out in early 2023.
“The reasons to sell the dollar are mostly generated by a sense of optimism that the world is healing,” Societe Generale SA strategist Kit Juckes wrote in a note to clients, pointing to developments around issues ranging from China’s reopening through to inflation. But he also warned that if investors think markets are being too complacent, they “should be wary of hangovers and euro softness in January.”
(Updates prices, adds comment from strategist.)
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.