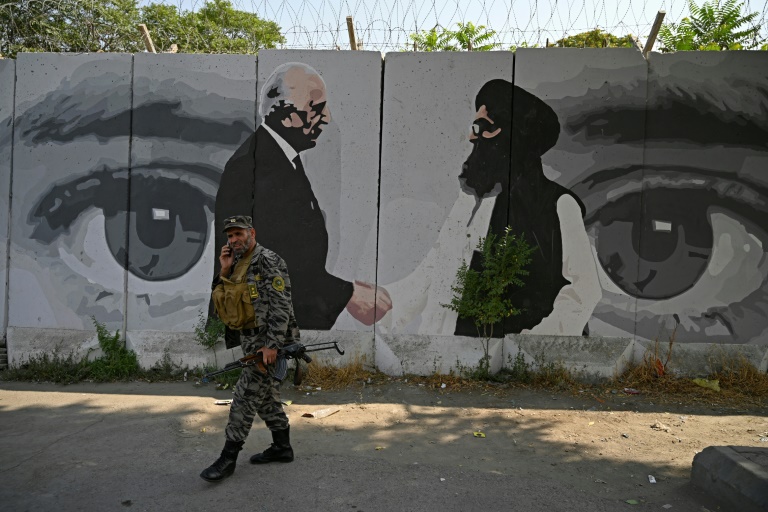
With US and international troops all but gone from Afghanistan and the Taliban making rapid gains, a number of players are positioning themselves for the next phase of the conflict.
Here is a rundown of what these powers, from the government in Kabul and local militias to regional nations, seek to gain or lose in Afghanistan as fighting intensifies for control of the war-weary country:
– Afghan security forces –
Thinly stretched with supply lines strained, the Afghan security forces have come under immense pressure in the final stages of the US military withdrawal.
Afghan troops are facing blistering attacks from the Taliban, including onslaughts on positions in the militants’ southern strongholds and a lightning offensive in the north.
But government forces continue to maintain control over the country’s cities, with most territorial losses in the sparsely populated rural areas.
“Many of the districts that have fallen were low-hanging fruit — remotely positioned and difficult to resupply or reinforce, with little strategic military value,” said Andrew Watkins, a senior analyst on Afghanistan for the International Crisis Group.
The Afghan military’s ability to weather the remaining months of the summer fighting season will likely be crucial to their long-term staying power.
Crucially, the US withdrawal means Afghan forces have lost vital American air support.
“Essentially, this year the war will be the war over districts and highways,” said Tamim Asey, the executive chair of the Kabul-based Institute of War and Peace Studies.
“Next year, we could potentially see that the Afghan Taliban might focus on provincial capitals and major urban centres.”
– The Taliban –
Never has the jihadist movement appeared so strong since being toppled by US forces two decades ago.
The group has executed a successful string of offensives across Afghanistan, capturing fully or partially about 100 out of more than 400 districts at a dizzying rate since early May.
The international community blames the Taliban for stalling landmark peace talks with the Afghan government in Doha.
Instead of a political settlement, the insurgents seem focused on positioning their troops for a military takeover.
“Strategically, it makes sense that they would test the Afghan security forces in the absence of US support to see how far they can get,” said Jonathan Schroden, director of the military think tank CNA’s Countering Threats and Challenges Program.
The Taliban appear to be united, operating under an effective chain of command, despite perennial rumours of splits among the group’s leadership.
– President Ashraf Ghani –
Known for his academic disposition and infamous temper, Ghani is said to be increasingly isolated at a moment when he is in desperate need of allies.
He has remained defiant despite mounting pressure on his government in the face of territorial losses.
“He was the creature, the man of the Americans, but he is now considered to be uncontrollable and an obstacle to the peace process,” a Western diplomat in Kabul said.
A recent shakeup of the country’s defence and interior ministries pulled his supporters closer, and may prove pivotal to his future political survival along with continued backing from Washington.
However, many of his team, who have spent years living abroad, are accused of being out of touch with the complex fabric of Afghan society.
Still, a recent trip to the White House saw Ghani secure promises of billions of dollars in security and humanitarian assistance.
– The warlords –
Afghanistan’s warlords may be waiting to make a comeback as the country’s security forces increasingly look to militia groups to bolster their depleted ranks.
As the Taliban battered their way through the north in June, a call for national mobilisation was sounded, with thousands taking up arms in scenes reminiscent of the 1990s civil war.
“The recent calls for such mobilisation will also likely increase fragmentation on the republic side and undermine command and control, putting civilians at increased risk,” said Patricia Gossman, the associate Asia director for Human Rights Watch.
Militia leaders may attempt to leverage their past contacts with foreign intelligence agencies to secure cash and weapons in exchange for on the ground reconnaissance.
New strongmen among Afghanistan’s ethnic minorities have also begun arming and training recruits, which may further inflame the country’s deep ethnic and sectarian divisions.
– Regional countries –
A new front in the region’s great game is opening with neighbouring countries looking to influence momentum on the ground in Afghanistan while also courting the conflict’s likely winners.
Pakistan has backed the Taliban for decades and may finally be able to cash its chips in a future government the insurgents either participate in or lead.
Islamabad’s major goal will focus on preventing arch-rival India from establishing any influence and posing a threat to its western border.
Iran is also hedging its bets.
After nearly going to war with the Taliban in the 1990s, Tehran has engineered considerable clout over at least one major faction within the group.
It also retains links with warlords who fought the Taliban during the country’s civil war.
“Some in Iran and Pakistan might certainly wish their favourites to get a bigger portion of the pie,” said Asad Durrani, the former head of Pakistan’s formidable spy agency.
“I doubt if the Taliban will let them have their way.”