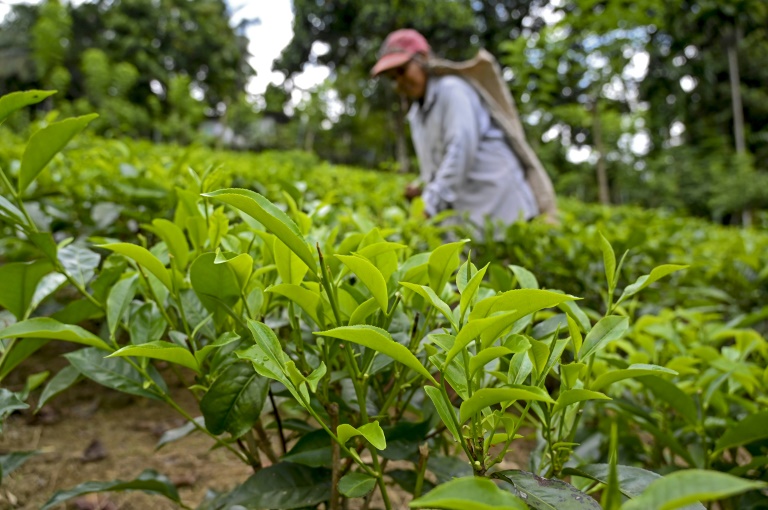
Crisis-struck Sri Lanka’s vital tea exports have dropped to their lowest level in 23 years, official figures showed Wednesday, hit by a fertiliser ban and the war in Ukraine.
Tea is the island nation’s biggest export commodity, bringing in about $1.3 billion annually before the current economic downturn, the worst since independence in 1948.
But a bungled ban on fertiliser imports last year — introduced in a doomed effort to save foreign currency and avoid a debt default — hit growers hard, with production falling 18 per cent on-year for the period from November 2021 to February 2022.
Customs data showed that first-quarter exports in 2022 correspondingly plunged to 63.7 million kilos (140 million pounds), down from 69.8 million kilos in the January-March period last year.
The tally was the lowest since the first quarter of 1999, when the country shipped out 60.3 million kilos of tea.
Export earnings for the first quarter also declined, to $287 million from $338 million.
Tea brokering firm Asia Siyaka blamed the drop on the agro chemical ban, which was portrayed by the government as a push to turn Sri Lankan farming 100-percent organic.
The ban was lifted by October following backlash from the industry, but farmers were left unable to access imported fertiliser as the country simultaneously ran out of dollars.
Industry officials added that about 10 percent of Sri Lanka’s tea exports had also been affected by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Both countries are top buyers of the island’s aromatic black tea.
The country of 22 million lacks enough foreign currency to finance even the most essential imports such as food, fuel and medicines.
Dire shortages and galloping inflation have led to widespread protests calling for President Gotabaya Rajapaksa to step down.