(Bloomberg) —
If you’re not seated at the table, you’re on the menu.
That old saying about the cutthroat nature of trade negotiations will be put to the test next week when officials gather in Geneva for the first meeting of the World Trade Organization’s highest decision-making body in nearly five years.
The goal of the WTO’s 12th ministerial conference is to conclude small but symbolically important deals to show that the headquarters of rules-based globalization is still capable of rallying countries to act together to solve problems.
The WTO’s leader, Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, has urged nations to conclude a handful of deliverables at the meeting, namely:
- an agreement to curb harmful fishery subsidies
- a framework to expand global access to vaccines
- a package to help address the global food crisis
- a renewal of the WTO’s ban on e-commerce duties and
- a work program to improve the WTO’s functioning.
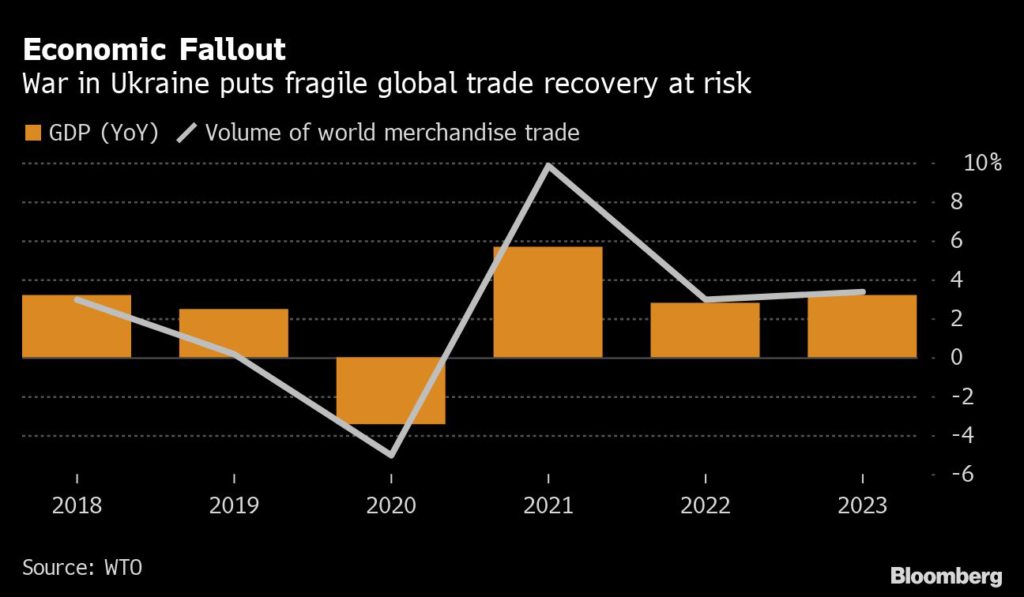
But the backdrop of these talks is marked with division and urgency. It will take place amid the simultaneous crises of surging inflation, war, disease and potential famine — when the need for collective action couldn’t be higher.
“The current geopolitical situation shows that the WTO is needed, and provides the WTO with an important opportunity,” European Trade Commissioner Valdis Dombrovskis told parliamentarians last month.
Global Fragmentation
While the WTO is no stranger to disappointment, any failure to reach agreements aimed at increasing vaccine production, averting a food crisis, or curbing overfishing will further cement the view that the WTO is no longer a viable forum to address the shortcomings of international commerce.
To be sure, a busted conference won’t be fatal to the WTO’s system of rules that govern more than $17 trillion worth of trade flows each year. But it could be the clearest sign yet that the world’s trading partners are redrawing allegiances along geopolitical lines — a new phase where might equals right and weak nations get trampled.
For some observers, this era began when the Trump administration raised tariffs on billions of dollars worth of goods shipped between America and its largest trade partners — namely China and the European Union.
Then, during the pandemic, many nations pursued their own nationalistic tendencies, like prioritizing the sourcing of critical health products, food supplies and vaccines for their own citizens instead of sharing them for the greater good.
The latest turn came when Russian President Vladimir Putin’s military started a war in Ukraine, marking a paradigm shift: For the first time, one WTO member invaded another.
Russia’s assault and the West’s sanctions have further disrupted the global economy by increasing the costs of doing business, pushing up the cost of living, and adding pressure to the world’s historically stressed supply chains.
‘Friend-Shoring’
“Fragmentation is going to stay,” said Robert Koopman, the WTO’s chief economist. “What we’re going to see is this reorganized globalization, with this recognition that there are these additional costs around uncertainty.”
The trend isn’t entirely new, but events of the past few years have accelerated the move away from multilateralism toward regional blocs of influence.
Key examples in the trade world include the 11-nation Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for a Trans-Pacific Partnership, the 15-nation Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, and the 54-nation African Continental Free Trade Area.
The US and others are pursuing an agenda of “friend-shoring,” which aims to shift manufacturing and trade flows away from authoritarian regimes like China and Russia, to countries that share the same economic and security concerns.
WTO Irrelevance
In the face of all these sweeping changes, the WTO — an organization founded on the premise that trading nations don’t go to war with each other — is practically helpless.
Under Trump, the US paralyzed a key component of the WTO’s dispute settlement system, which has prevented nations from obtaining final trade justice and increased the risk of tit-for-tat trade wars.
And the WTO’s consensus principle — whereby multilateral agreements must be approved by all 164 WTO members — is simply not working.
“It is very difficult to agree to things multilaterally and that has been plaguing the WTO,” Okonjo-Iweala acknowledged during this year’s World Economic Forum.
Many nations, India in particular, have found it to be more advantageous to block consensus WTO agreements in order to subsidize and protect their domestic industries.
But India isn’t entirely to blame. The US, which was the original architect of the global trading system, “has not demonstrated a willingness to make the necessary investment in the WTO to revive it as a negotiating forum,” former WTO Deputy Director-General Alan Wolff wrote last month.
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.