Schools and rallies bombed, hospitals targeted and commuters ambushed: for years, the Hazara community has suffered some of Afghanistan’s most violent assaults.
Now, with the Taliban back in control, the majority Shiite Muslim group fears the Sunni hardliners may again turn on them — just as they did during their last regime in the 1990s.
And even as the Taliban have pledged a softer rule this time, a statue of a prominent Hazara leader was vandalised just days after the Islamists swept back into power.
Here is a brief history of the community:
– Who are the Hazaras? –
Hailing from the country’s rugged central highlands, the Hazaras are believed to trace their lineage from Genghis Khan’s Mongol invaders who ransacked Afghanistan in the 13th century.
Comprising between 10 to 20 percent of the country’s 38 million people, Hazaras have been marginalised for their faith in a country riven by deep divisions.
By some estimates, nearly half of the Hazara population was wiped out in the late 19th century, with many later enslaved during the conquest of their traditional homeland by Pashtuns, the country’s biggest ethnic group.
Throughout the centuries, the group has been subjected to slavery, religious and economic persecution, as well as displacement and ethnic cleansing.
They have also been targeted by an array of different groups during the past four decades of conflict, including the vicious shelling of their areas.
Hazara militia fighters were accused of carrying out atrocities of their own during the civil war that followed the withdrawal of the Soviet army in the late 1980s.
During the Taliban’s scorched-earth takeover of the country in the late 1990s, thousands of Hazaras were believed to have been slaughtered by the militants.
– Why are they targeted? –
The Hazaras make up the bulk of the country’s Shiite minority, which has historically been despised by Sunni hardliners who consider the sect heretics.
The group has also been accused of being too closely allied to neighbouring Iran, and tens of thousands have moved over the years as economic migrants to work mostly menial jobs.
Thousands of Hazaras have been trained by Iranian security forces and deployed with Shiite militias in Syria’s civil war over the past decade.
Last year, the Iranian foreign minister called Hazara militia fighters the “best forces with a military background” that could be used against the Islamic State group in Afghanistan.
– What happens to them when US troops leave? –
Few groups benefited from the order established by the US overthrow in 2001 of the Taliban as much as the Hazaras.
They were able to put their children in schools — including their daughters — and entered the political scene and workforce in unprecedented numbers.
But those gains remained tenuous.
The group took the brunt of escalating violence as Islamic State suicide bombers targeted their mosques, schools, rallies and hospitals in western Kabul’s Hazara enclave of Dasht-e-Barchi, killing hundreds of people.
Fearing they will again be slaughtered when international troops exit Afghanistan this summer, some in the community have started to rearm — with a small militia based in Wardak province recruiting and training Hazaras to fight back.
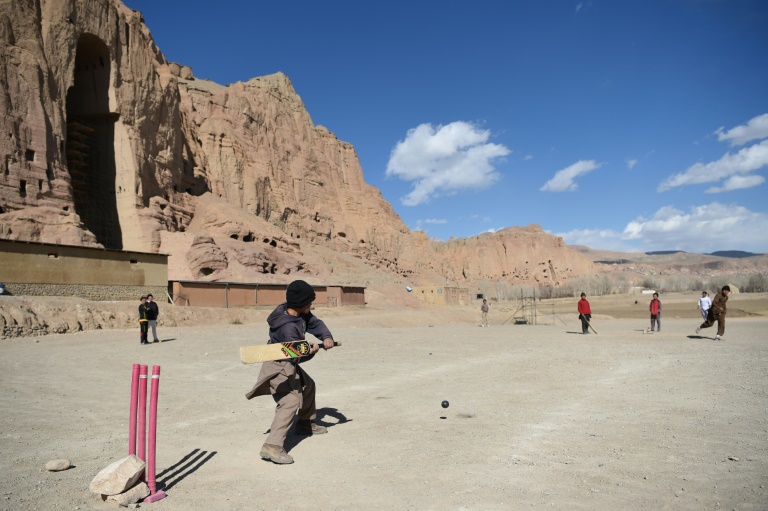
Days after the Taliban returned to power, the statue of a prominent Hazara leader in Bamiyan — where the famed Buddhas were also destroyed two decades ago — was decapitated.
The incident spurred fears that the militants still hold a grudge against the community, and that they may crack down again soon.