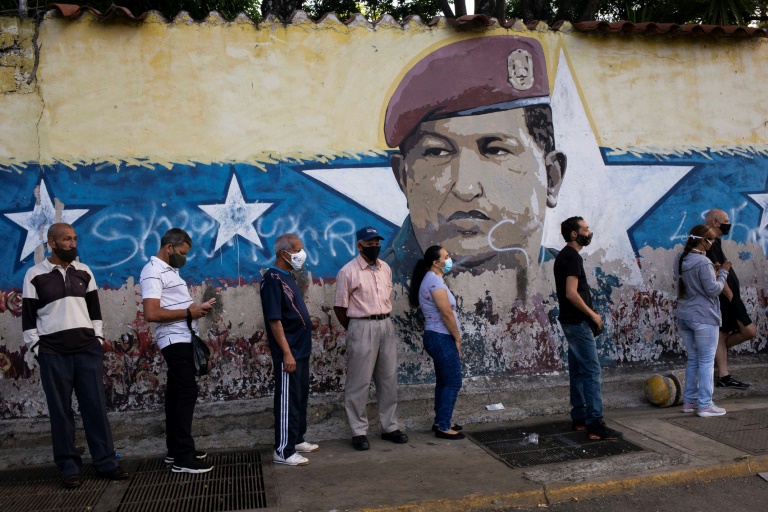
An EU observer mission on Tuesday reported irregularities in Venezuelan elections for governors and mayors over the weekend, in which opposition parties participated for the first time since 2017.
Despite “better conditions” than in previous elections, the observers noted a “lack of adherence to the rule of law.”
Mission head Isabel Santos told reporters that “some laws affected the equality of conditions, the balance and the transparency of the elections” and this within the context of a “lack of judicial independence.”
The government of President Nicolas Maduro, whose 2018 election is not recognized by part of the international community, won a landslide victory in Sunday’s ballot, which was overseen by EU observers for the first time in 15 years.
Weakened and divided, the opposition won only three of 23 states, although this significantly included oil-rich Zulia — the country’s most populated region whose capital Maracaibo is Venezuela’s second-largest city.
Santos said the electoral campaign had been marked by a “widespread use of state resources” and noted “arbitrary disqualifications” of candidates.
Observers had furthermore witnessed ruling party agents create so-called “red spots” or illegal control points near several voting stations, she said.
The mission said it lamented the shooting death of one voter at a polling station, which the government said was unrelated to the election.
– ‘Grossly skewed’ –
Leftist Maduro, whose deeply controversial presidency has seen the South American nation targeted by economic sanctions, has sought a relaxation of the punitive measures through careful shows of goodwill and democratic intent.
With hundreds of millions of dollars of its funds frozen abroad, Venezuela wants to be able to sell its petroleum more easily — the United States is historically its biggest customer — and to end limits on imports.
The government has made a calculated series of concessions, opening negotiations with the opposition, and inviting election observers from the EU, the United Nations and the US-based Carter Center to witness Sunday’s vote in a bid to boost its legitimacy.
The opposition, which for the past three years had boycotted elections they said were neither free nor fair, agreed to take part in Sunday’s race after receiving assurances from the government.
Opposition leaders hoped to raise their profile through participation, and to gain support ahead of presidential elections set for 2024, but were hamstrung by divisions within their own ranks.
On the eve of the vote, Maduro had warned that the European Union had no authority to give a “verdict” on the process in a country that is prickly about its “sovereignty” and often accuses the United States of interventionism.
“All international escorts must respect the laws of Venezuela, and must strictly respect the regulations of the electoral power that invited them,” the president said.
The United States, which also had observers in Venezuela, on Monday called the vote “grossly skewed.”
Venezuela, a once-rich oil producer, is battling its eighth year of recession and hyperinflation that reached nearly 3,000 percent in 2020 and more than 9,500 percent the year before, according to central bank figures.
Three in four Venezuelans live in extreme poverty, according to a recent study, with the economic crisis made worse by US sanctions and the coronavirus pandemic.
Millions have left the country in recent years to try their luck elsewhere.